Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
Tags
- URP
- OculusMotionVectorPass
- 게임 수학
- URP로 변경
- 작업 집합
- 가상 바이트
- ASW(Application SpaceWarp)
- Toon Shader
- VR
- 3d
- Cell Look
- Three(Two) Tone Shading
- 프로그래밍 기초
- 벡터
- Virtual Byte
- 메모리 누수
- Cell Shader
- 개인 바이트
- Rim Light
- AppSW
- Cartoon Rendering
- Windows Build
- ColorGradingLutPass
- Specular
- Private Bytes
- C언어
- working set
Archives
- Today
- Total
WinCNT
자료구조 - 그래프 본문
셀과 노드
자료구조의 기반은 셀이거나, 노드
여러 자료 구조도 결국은 셀이나, 노드를 기반으로 만들었다고 볼 수 있다
cell = 데이터의 집합 = 배열
구조체, 배열...
선형적
인덱스로 찾기
노드 = 포인터로 연결 = 리스트
메모리(물리적)으로는 선형적이 아니지만
논리적으로는 선형적일 수도 있음
포인터로 찾기
트리
힙은 셀을 사용(효율 문제)
이진 트리 등은 노드 사용(효율 문제)
그래프
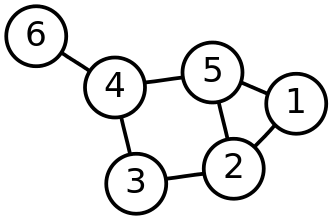
연관 관계를 만들면 그것이 그래프이다
서로 연결이 되서 탐색할 수 있다
(참고로 트리도 그래프의 일종)

그래프 기반의 탐색
그래프 기반의 탐색 ⇒ 경로 탐색
경로 탐색은 정점과 정점 사이의 경로를 탐색하는 것이므로 정렬은 하지 않는다
여태까지의 알고리즘은 보통 값을 탐색하는 것이었다
그러기 위해 삽입, 삭제, 탐색 시 데이터를 정렬하기도 했다
예) 최소값, 최대값
대표적인 그래프 기반의 경로 탐색 알고리즘
- 너비 우선 탐색 (BFS)
- 하나의 시작 정점으로부터 모든 다른 정점까지의 최단 경로 탐색
- 다익스트라 (Dijkstra)
- 너비 우선 탐색을 기반으로 정점 사이의 가중치를 적용하여
하나의 시작 정점으로부터 모든 다른 정점까지의 최단 경로 탐색
- 너비 우선 탐색을 기반으로 정점 사이의 가중치를 적용하여
- A*
- 다익스트라 알고리즘을 확장하여 두 정점 사이의 최단 경로 탐색
- A*가 유명한 이유는 비교적 자료 구조로부터 자유롭기 때문
(그리드 기반이면 A*보다 적합한 알고리즘도 있긴 함)
그래프 만들기(Build Graph) 예제 코드
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm> // sort
using namespace std;
typedef struct Node
{
char name;
//Node* accessibleNode[10];
list<Node*> accessibleNode;
} Node;
// 그래프 빌드를 위한 배열
Node* Graph[10];
/// <summary>
/// 그래프 초기화
/// </summary>
void InitGraph()
{
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(Graph) / sizeof(Graph[0]); i++)
{
Graph[i] = nullptr;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 접근 가능 노드 목록의 정렬을 위한 기준
/// </summary>
/// <param name="lhs"></param>
/// <param name="rhs"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
bool nameComp(Node* lhs, Node* rhs) {
return lhs->name < rhs->name;
}
/// <summary>
/// 입력값에 따라 그래프를 빌드
/// </summary>
/// <param name="name"></param>
void BuildGraph(char input1, char input2)
{
int indexInput1 = input1 - 'A';
int indexInput2 = input2 - 'A';
// 그래프에 노드가 없을 시 생성
if (Graph[indexInput1] == nullptr)
{
Graph[indexInput1] = new Node();
Graph[indexInput1]->name = input1;
}
if (Graph[indexInput2] == nullptr)
{
Graph[indexInput2] = new Node();
Graph[indexInput2]->name = input2;
}
// 첫번째 입력값 노드를 찾고 그 노드의 접근 가능 노드 목록에
// 두번째 입력값 노드를 추가(중복인 경우는 처리 안 함)
// 중복된 경로 설정인지 확인
auto iter = find(Graph[indexInput1]->accessibleNode.begin(),
Graph[indexInput1]->accessibleNode.end(),
Graph[indexInput2]);
// 중복된 경로가 없는 경우
if (iter == Graph[indexInput1]->accessibleNode.end())
{
// 접근 가능 노드 목록에 두번째 입력값 노드를 추가
Graph[indexInput1]->accessibleNode.push_back(Graph[indexInput2]);
// 접근 가능 노드 목록을 정렬함
// sort(Graph[indexInput1]->accessibleNode.begin(), Graph[indexInput1]->accessibleNode.end());
Graph[indexInput1]->accessibleNode.sort(nameComp);
}
}
void printGraph()
{
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(Graph) / sizeof(Graph[0]); i++)
{
if (Graph[i] != nullptr)
{
cout << Graph[i]->name;
if (Graph[i]->accessibleNode.size() > 0)
{
cout << " => ";
for (auto iter = Graph[i]->accessibleNode.begin();
iter != Graph[i]->accessibleNode.end(); iter++)
{
cout << (*iter)->name << " ";
}
}
cout << endl;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
InitGraph();
char input1, input2;
while (true)
{
cout << "A~J까지의 알파벳 중 2개를 입력해 주세요\n";
cin >> input1;
cin >> input2;
// 잘못된 입력일 경우는 다시 입력하게 처리
if ((input1 < 'A' || input1 > 'J')
|| (input2 < 'A' || input2 > 'J')
)
{
cout << "잘못된 입력입니다.\n";
continue;
}
BuildGraph(input1, input2);
printGraph();
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
SSS
'게임 프로그래밍(학습 내용 정리) > 자료구조와 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 경로 탐색 알고리즘 - 너비 우선 탐색(BFS, Breadth First Search) (0) | 2022.01.18 |
|---|---|
| 자료 구조에 대해서(보충) (0) | 2022.01.18 |
| 메모리 정렬 (0) | 2022.01.11 |
| 자료 구조 - Hash (0) | 2022.01.03 |
| 페이지 교체와 알고리즘 (0) | 2022.01.03 |

